
The asset turnover ratio is calculated by dividing net sales or revenue by the average total assets. The asset turnover ratio measures how effectively a company uses its assets to generate revenues or sales. The ratio compares the dollar amount of sales or revenues to the company’s total assets to measure the efficiency of the company’s operations.
Asset Management Ratios: Definition, Formula, Example, More

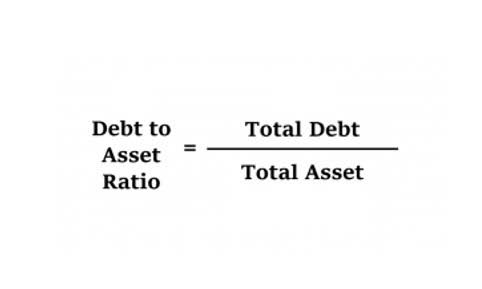
If Company B has a total debt of $1 million and a total assets of $4 million, its debt to asset ratio is 0.25. This means that 25% of the company’s assets are financed by debt, which implies a low leverage. Asset Turnover Ratio is a fundamental metric that plays a crucial role in assessing a company’s operational efficiency and overall financial health. It measures how effectively a company utilizes its assets to generate sales revenue. On the other hand, if a company’s industry has an asset turnover that is greater than 1 and the company’s ratio is 0.9; then the company is not doing well. In this case, a lower asset turnover ratio indicates that the company may not be using its assets efficiently.

How to Calculate Asset Turnover Ratio
- So, if you have a look at the figure above, you will visually understand how efficient Wal-Mart asset utilization is.
- The Asset Turnover Ratio evaluates how a company utilizes its assets to generate revenue or sales.
- A higher ATR generally suggests that the company is using its assets efficiently to generate sales, while a lower ratio may indicate inefficiency in asset utilization.
- Most importantly, these ratios consider the revenues of a company and neglect its profits.
Therefore, a higher value of this ratio is usually interpreted as a company using its assets well enough to generate its net sales or revenue. In this article, we will discuss the asset turnover ratio interpretation and how to interpret it with examples. Several factors can influence a company’s asset turnover ratio, which represents how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate sales.
- Creditors, on the other hand, want to make sure that the company can produce enough revenues from a new piece of equipment to pay back the loan they used to purchase it.
- While it is a type of asset turnover ratio, some stakeholders prefer only to consider the company’s fixed assets to evaluate its efficiency.
- In simple terms, the asset turnover ratio means how much revenue you earn based on the total assets.
- Generally, a low asset turnover ratio interpretation suggests that the company has problems with surplus production capacity, poor inventory management, or bad tax (or revenue) collection methods.
- FAT measures a company’s ability to generate net sales from its fixed-asset investments, namely property, plant, and equipment (PP&E).
- The fixed asset turnover is a ratio that can help you to analyze a company’s operational efficiency.
#6 – Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio
This metric analyzes a company’s ability to generate sales through fixed assets, also known as property, plant, and gross vs net equipment (PP&E). There are other turnover ratios, such as the fixed assets turnover ratio and working capital turnover ratio. In all cases the numerator is the same i.e. net sales (both cash and credit) but denominator is average total assets, average fixed assets, and average working capital, respectively. The asset turnover ratio is a metric that indicates the effectiveness of a company in utilising its owned resources to generate revenue or sales. The asset turnover ratio reveals the number of sales generated from each rupee of company assets by comparing the company’s gross revenue to the average total number of assets.
- A higher debt to asset ratio indicates that the company has more leverage, which means it is using more borrowed funds to finance its assets.
- It also makes conceptual sense that there is a wider gap between the amount of sales and total assets compared to the amount of sales and a subset of assets.
- The asset turnover ratio can also be analyzed by tracking the ratio for a single company over time.
- Paul Boyce is an economics editor with over 10 years experience in the industry.
- A higher ratio indicates that the company is using its assets effectively to produce more sales, while a lower ratio suggests inefficiencies in asset management.
- Asset turnover ratios differ between industry sectors, making it crucial to compare only companies within the same sector.
- Meredith is frequently sought out for her expertise in small business lending and financial management.
For instance, retail or service sector companies typically have smaller asset bases but generate higher sales volumes, resulting in higher average asset turnover ratios. To do so, divide the company’s net sales (or total revenue) by its average total assets formula during a specific period. An asset turnover ratio is a ratio that compares the total amount of a company’s net sales in dollar amount to the total amount of assets that was used to generate the stated amount of net sales. This means that an asset turnover ratio interpretation tells us how efficiently the assets of a company Bakery Accounting are deployed to generate revenue.

The higher the asset turnover ratio, the better the company is performing, asset turnover ratio since higher ratios imply that the company is generating more revenue per dollar of assets. The ratio measures the efficiency of how well a company uses assets to produce sales. Conversely, a lower ratio indicates the company is not using its assets as efficiently.